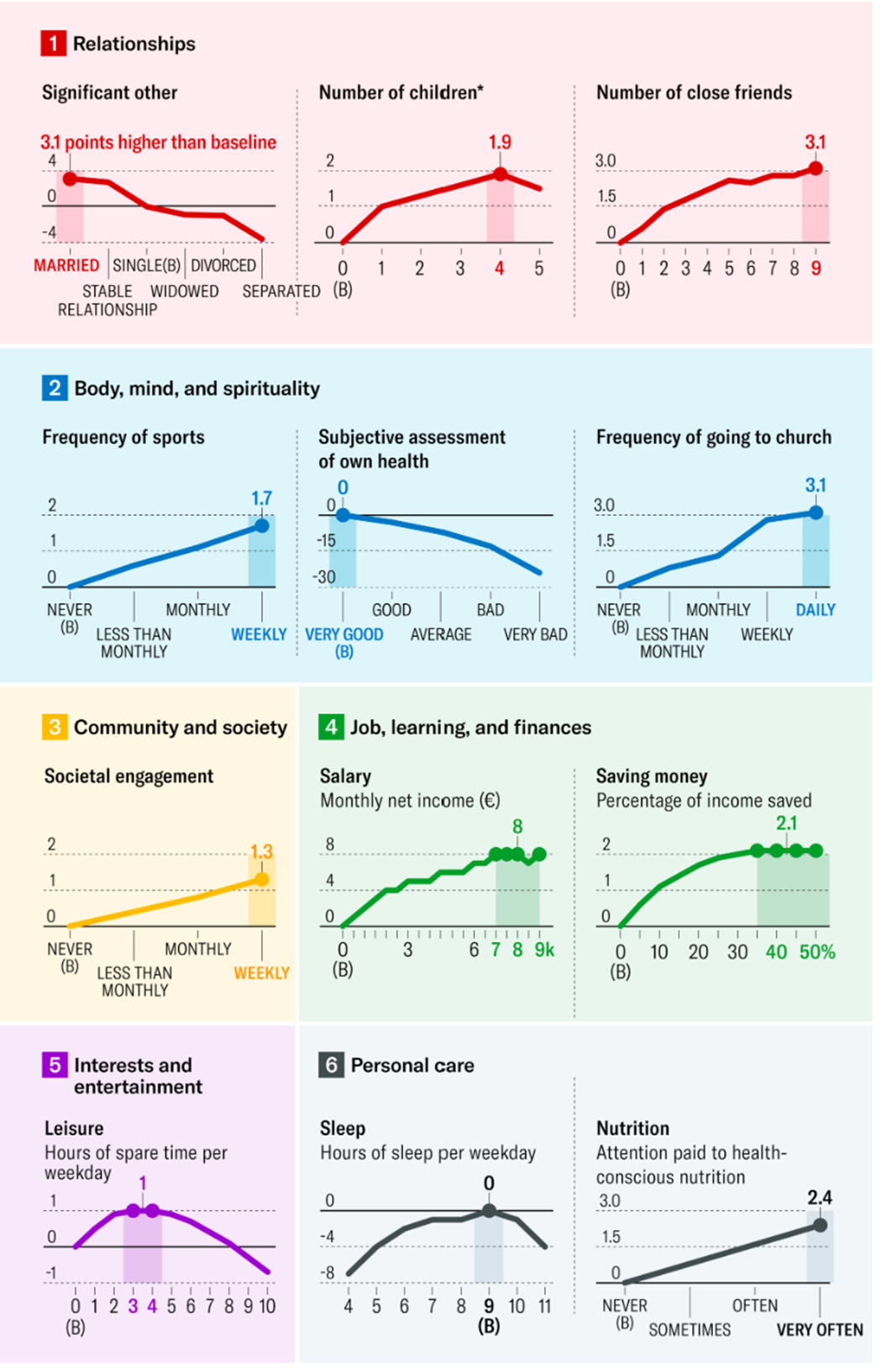
Double diamond design sprint methodology
Instruction guide
Introduction: A framework for validating success
The Double Diamond Design Sprint is a powerful problem solving and innovation framework that helps organisations develop, test, and refine ideas before committing significant time and resources. Originally developed by the UK Design Council in 2005, the Double Diamond provides a structured, user centered approach to innovation. It ensures that solutions are not only desirable (meeting real user needs), but also feasible (technically possible) and viable (commercially sustainable).
By integrating the Design Sprint methodology, developed by Google Ventures (GV), the process accelerates validation, enabling teams to prototype and test ideas rapidly. This approach increases the chances of success by ensuring that only the strongest, most viable solutions move forward, while ineffective ideas are identified and eliminated early.
The 'fail fast' principle is a crucial part of this methodology. By testing assumptions early, businesses can avoid costly mistakes and pivot quickly when necessary, ensuring that only solutions with real potential reach market launch.
When & where to use the Double Diamond Design Sprint
This methodology is ideal for:
- New product or service development – Ensuring solutions align with market needs.
- Business strategy and innovation – Creating viable business models.
- Startups & corporate innovation teams – Reducing risk and maximising impact.
- User experience (UX/UI) & digital transformation – Designing intuitive, effective solutions.
- Marketing & customer engagement strategies – Testing ideas before large scale investment.
By validating desirability, feasibility, and viability, the Double Diamond helps reduce risk and increase the likelihood of success.
Benefits of the Double Diamond Design Sprint
- Desirability – Ensures the idea meets genuine customer needs.
- Feasibility – Tests whether the idea can be realistically implemented.
- Viability – Assesses whether the idea is commercially sustainable.
- Fail fast, learn faster – Eliminates weak ideas before they become costly mistakes.
- Customer-focused innovation – Ensures solutions are user centered and impactful.
- Efficient resource allocation – Prevents wasted time and investment in unproven ideas.
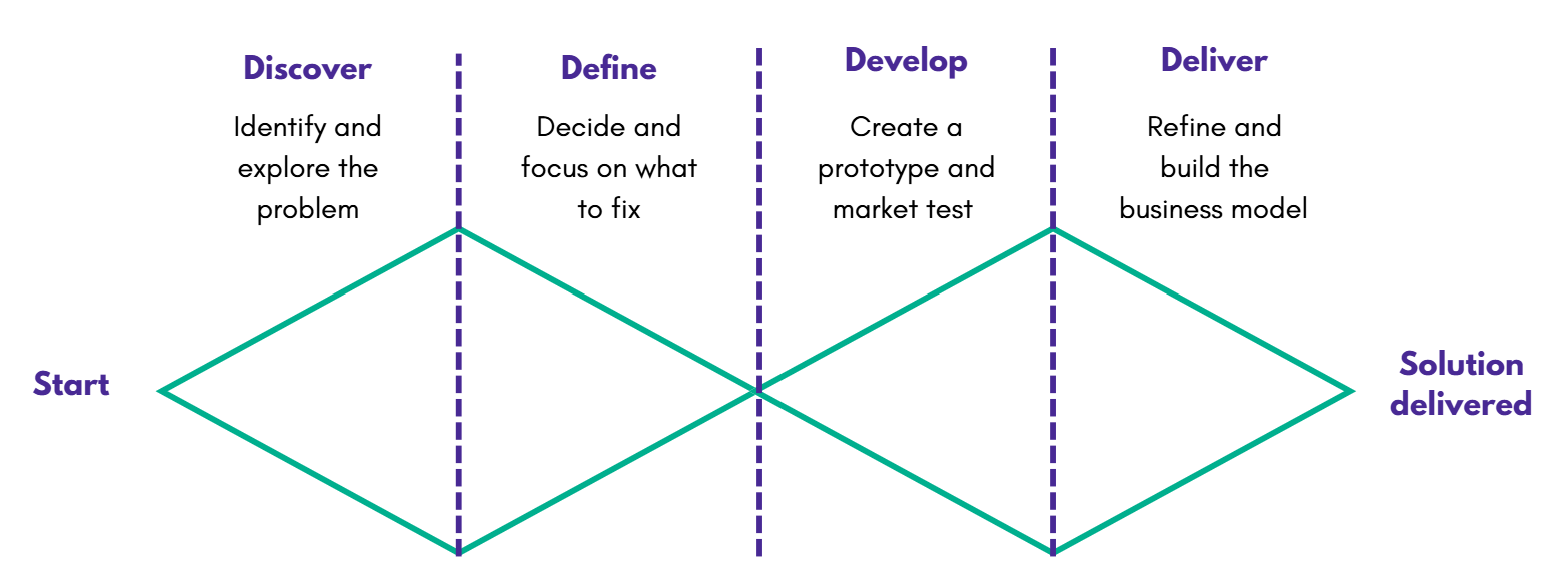
Step by step guide to the Double Diamond Design Sprint
The Double Diamond consists of four key stages, divided into divergent (expanding ideas) and convergent (narrowing ideas) thinking:
- Discover – Understand the problem (desirability validation)
- Define – Frame the challenge (desirability & feasibility validation)
- Develop – Ideate and prototype (feasibility validation)
- Deliver – Test, refine, and implement (viability validation)
Step 1: Discover (understanding the problem - desirability validation)
Goal: Gather insights to determine if the problem is real and worth solving.
Activities:
- Conduct user research (interviews, surveys, observations).
- Map customer journeys to understand pain points.
- Analyse market trends and competitors.
- Identify unmet needs and gaps in the market.
Key question: Do people actually need or want this?
Kill signal: If research shows there’s no clear user pain point or market demand, stop or pivot before moving forward.
Step 2: Define (framing the challenge - desirability & feasibility validation)
Goal: Focus on the most critical problem and ensure it can be solved effectively.
Activities:
- Identify key patterns and themes from research.
- Craft a problem statement to frame the challenge.
- Use how might we (HMW) questions to explore possible solutions.
- Prioritise core user needs and define key success criteria.
Key question: Is this a problem we can realistically solve?
Kill signal: If the challenge is too broad, unsolvable, or already well addressed, redefine or abandon the idea.
Step 3: Develop (generating & prototyping solutions - feasibility validation)
Goal: Generate and prototype potential solutions to test feasibility.
Activities:
- Conduct brainstorming (Crazy 8s, SCAMPER, etc.).
- Prioritise ideas based on feasibility and impact.
- Build low fidelity prototypes (wireframes, sketches, MVPs).
- Perform quick internal tests to refine early stage concepts.
Key Question: Can this be built with existing resources and technology?
Kill Signal: If prototyping reveals major technical or operational barriers, stop or pivot before investing further.
Step 4: Deliver (testing & refining the solution - viability validation)
Goal: Validate whether the solution can succeed in the real world.
Activities:
- Conduct usability testing with real users.
- Observe how users interact with the prototype.
- Gather qualitative and quantitative feedback.
- Iterate and refine based on test insights.
Key question: Does this solution work effectively for real users?
Kill signal: If testing reveals consistent failure, poor user adoption, or negative feedback, pivot or stop development.
Step 5: Market testing (validating viability at scale)
Goal: Test the commercial viability of the solution before full scale investment.
Activities:
- Soft launch or beta test with a small user group.
- Run A/B testing to compare variations.
- Gather real world performance data and measure user engagement.
- Test pricing, messaging, and market positioning via digital campaigns.
- Use landing pages, pre orders, or crowdfunding to gauge demand.
Key question: Will people pay for or adopt this solution at scale?
Kill signal: If
demand is low, acquisition costs are too high, or customers aren’t engaging,
stop or adjust the strategy.
Fail fast, learn faster: When to kill an idea
One of the biggest advantages of the Double Diamond Design Sprint is its ability to eliminate weak ideas early, saving time, money, and effort. Knowing when to stop is just as important as knowing when to push forward.
Red Flags that signal it's time to kill an idea:
- No clear user pain point or need (Desirability fails).
- Solution isn’t technically feasible with available resources (Feasibility fails).
- No
willingness to pay or market traction (Viability fails).
- Testing reveals high friction, low adoption, or significant negative feedback.
- The idea has too many competitors already doing it better.
Pivoting vs. killing an idea:
- If one part of the idea is strong, pivot and refine.
- If all signs point to failure, kill the idea and move on.
Final thoughts: Increasing success through smart validation
The Double Diamond Design Sprint is more than just an innovation framework—it’s a strategic validation tool that helps businesses and entrepreneurs launch only the best, most viable ideas. By systematically testing desirability, feasibility, and viability, this approach:
- Reduces risk by filtering out weak ideas.
- Saves resources by preventing wasted effort.
- Increases success rates by ensuring ideas meet real user needs.
- Encourages innovation by embracing experimentation and iteration.
Whether you’re a startup, corporate innovator, or product designer, the Double Diamond Design Sprint can streamline your innovation process, boost success, and ensure your ideas make an impact.